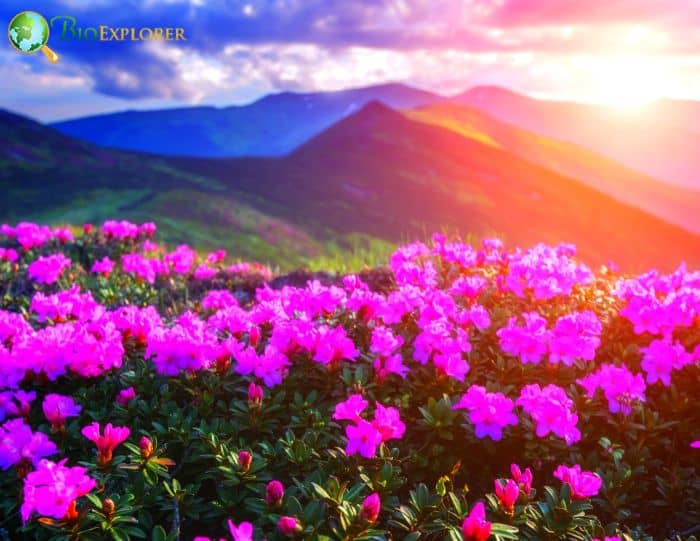
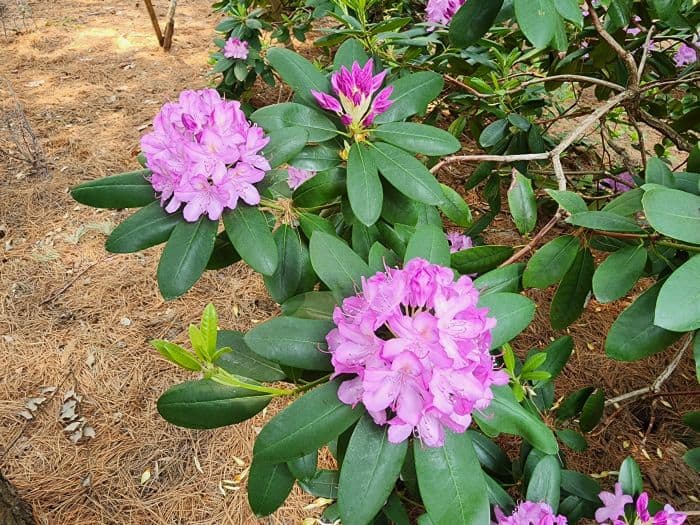
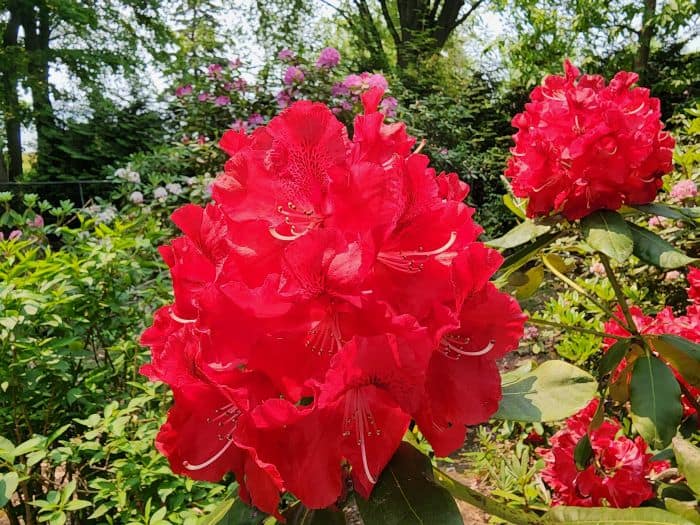
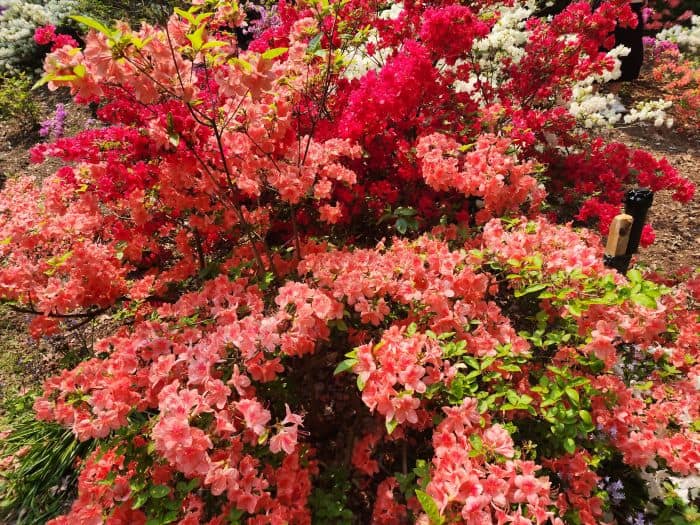
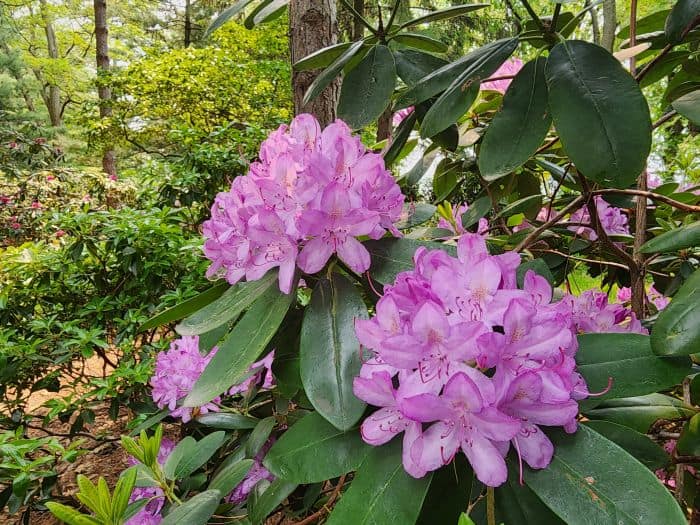
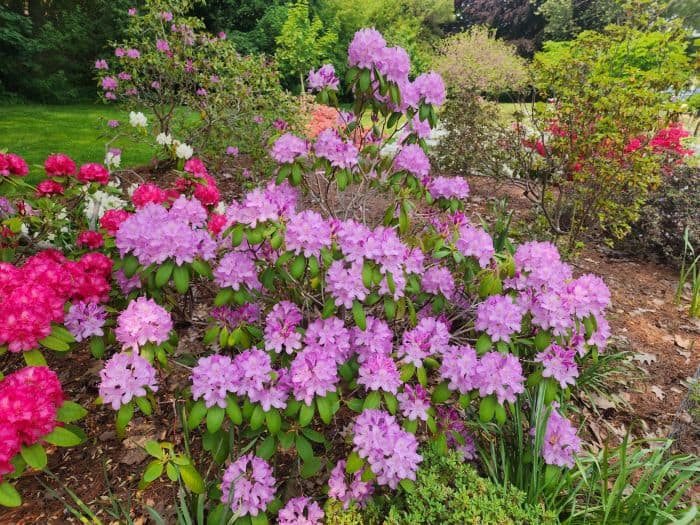
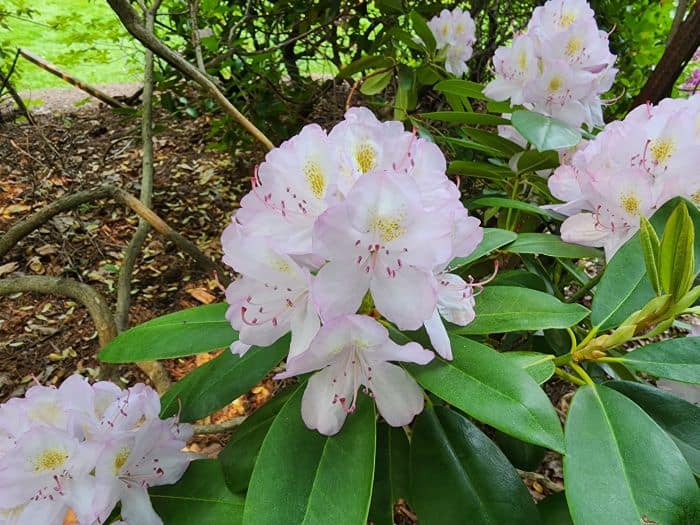
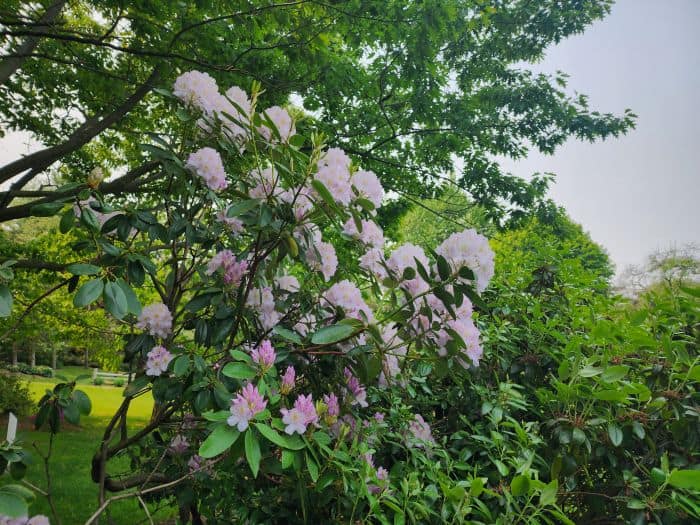
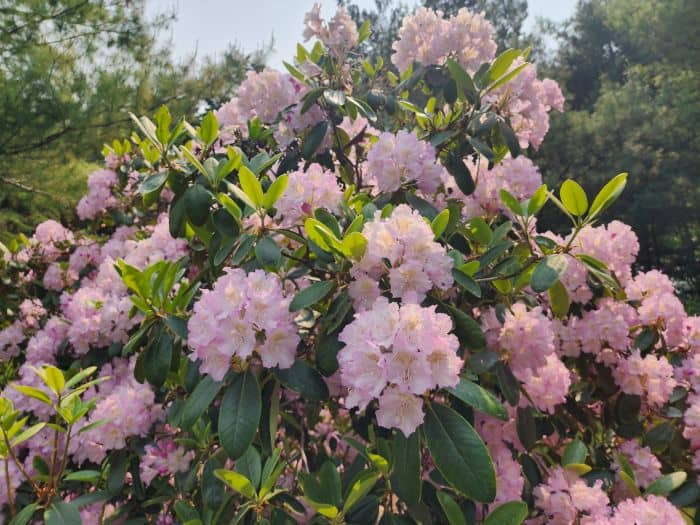
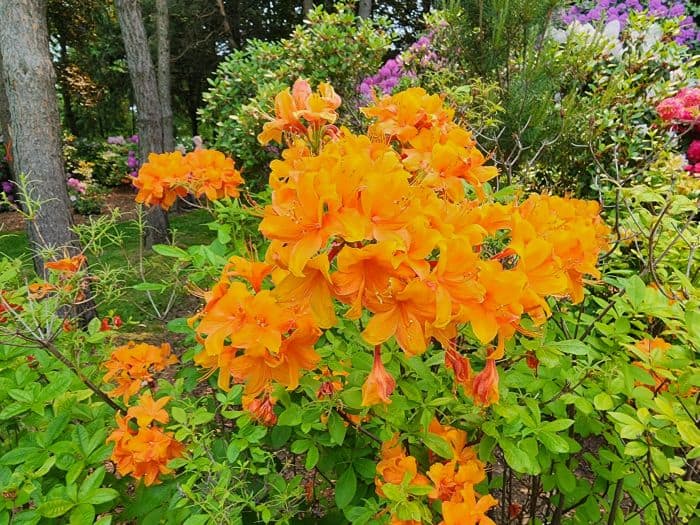
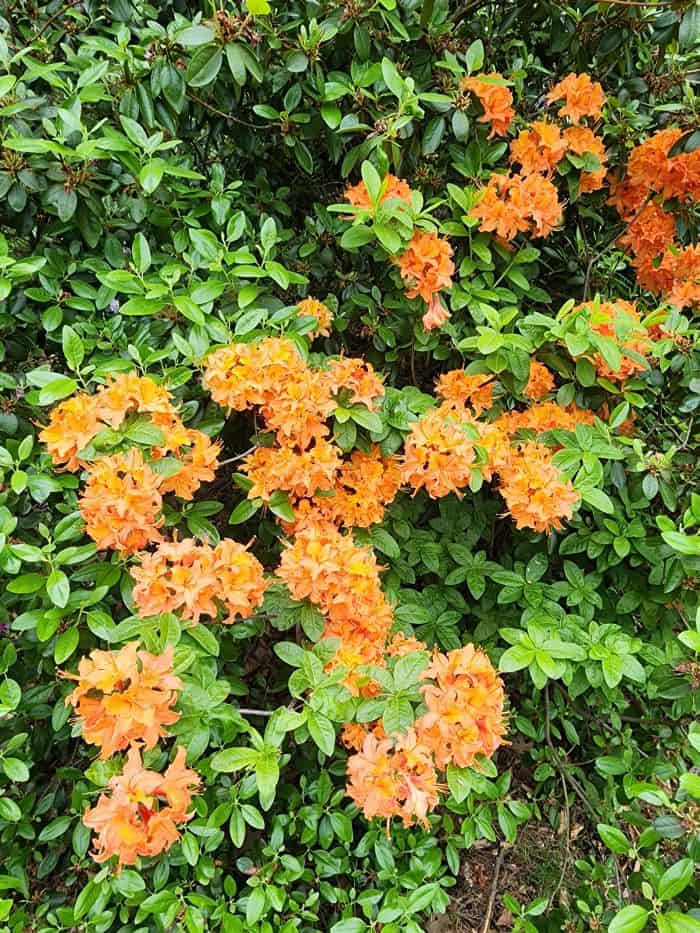
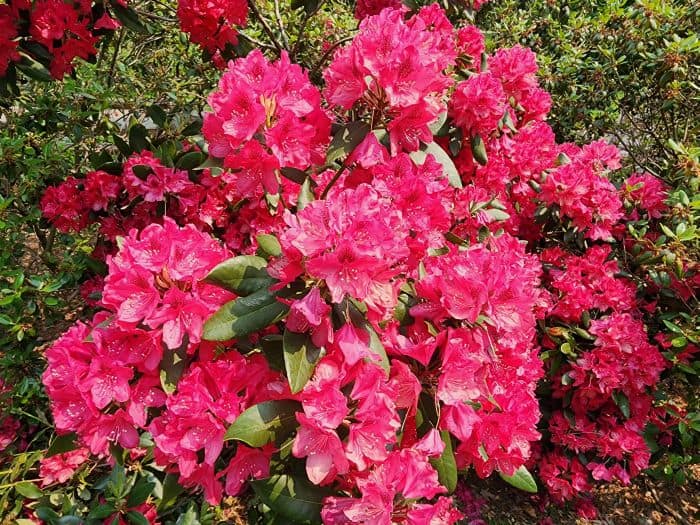
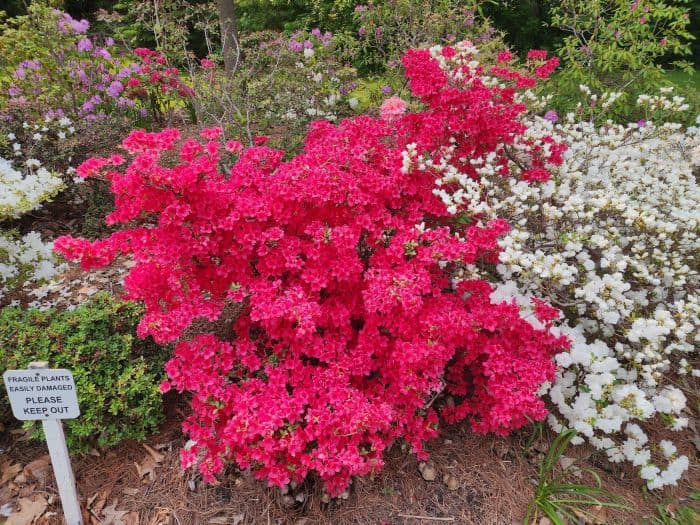
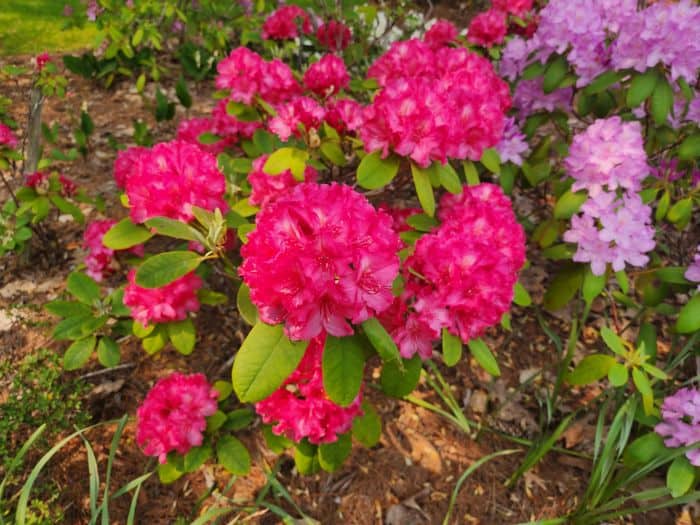
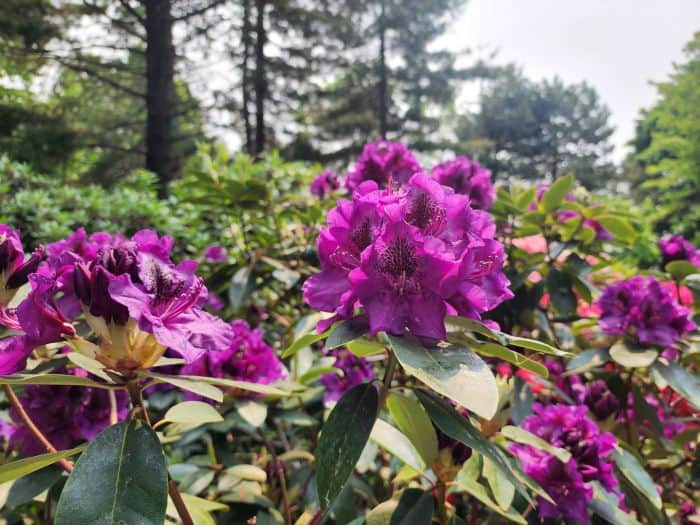
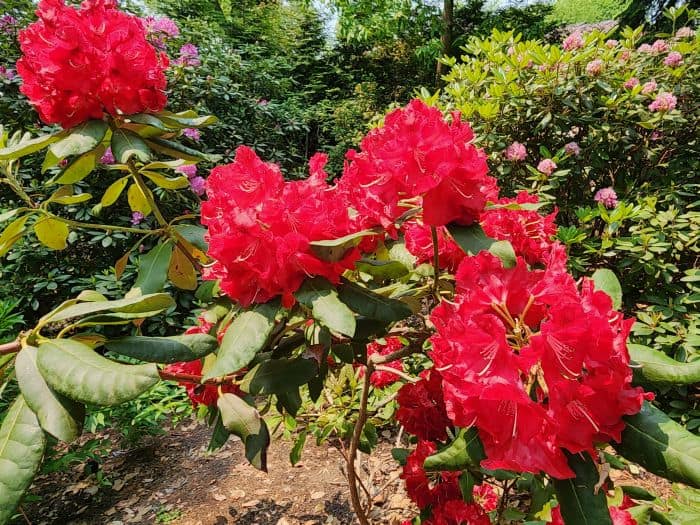
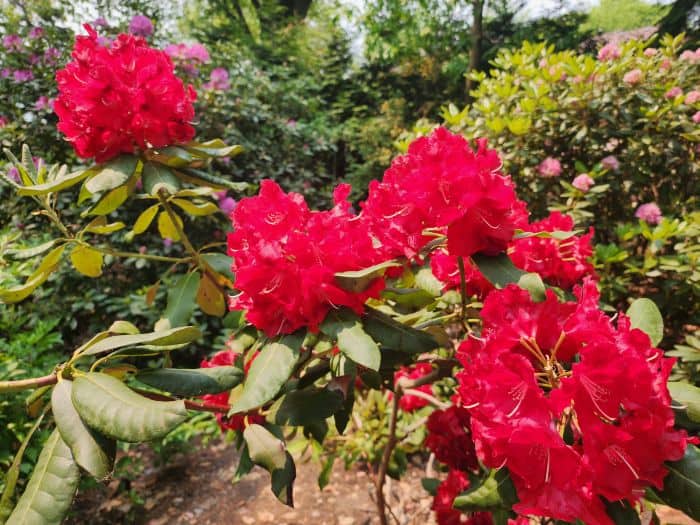
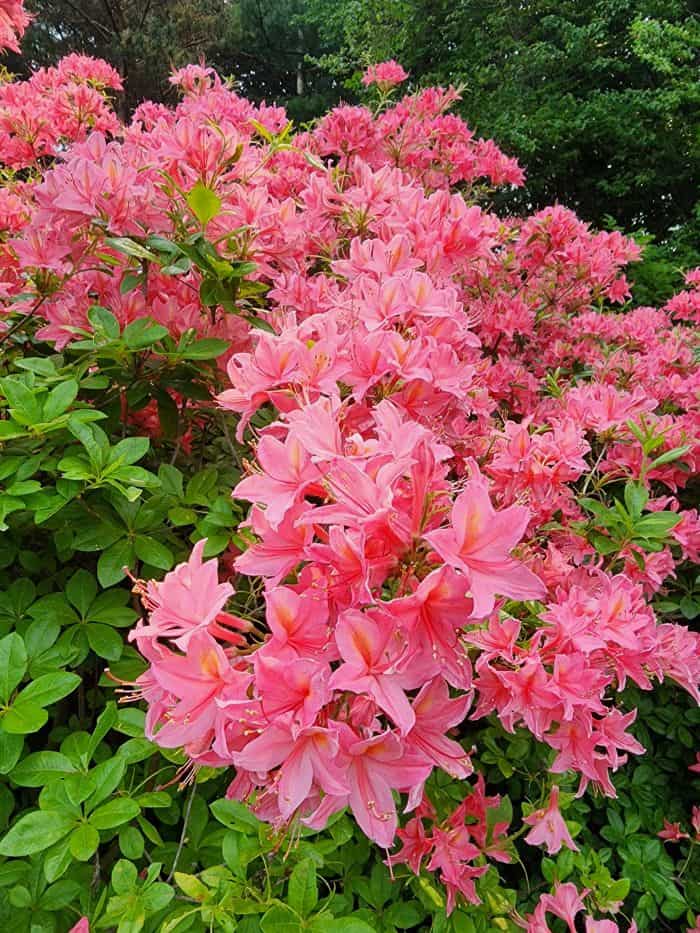
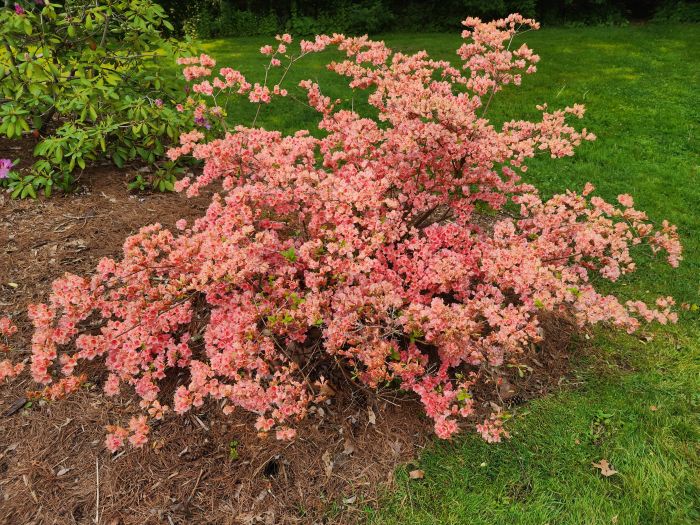
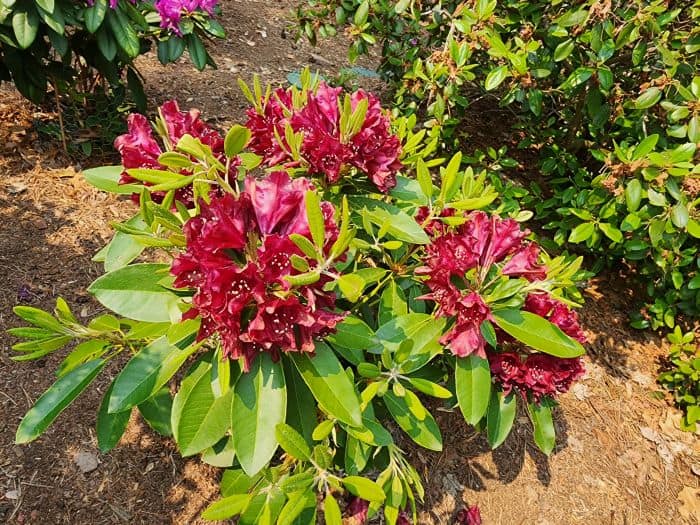
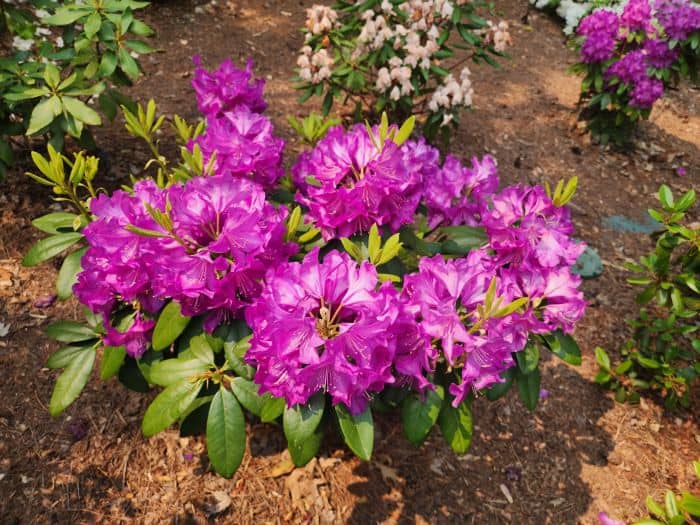
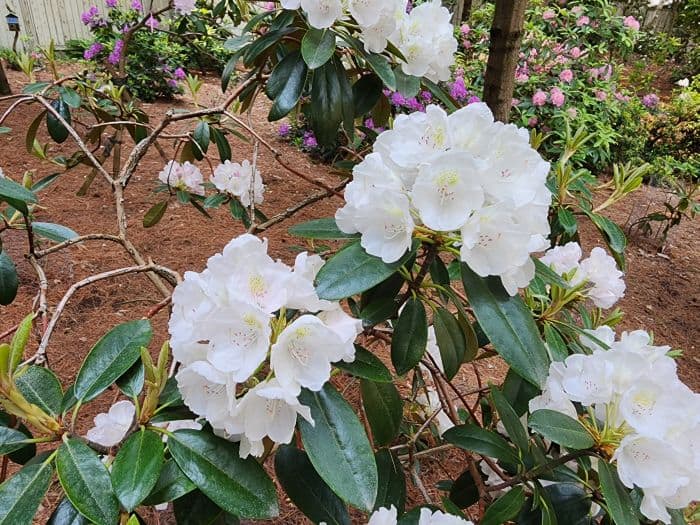
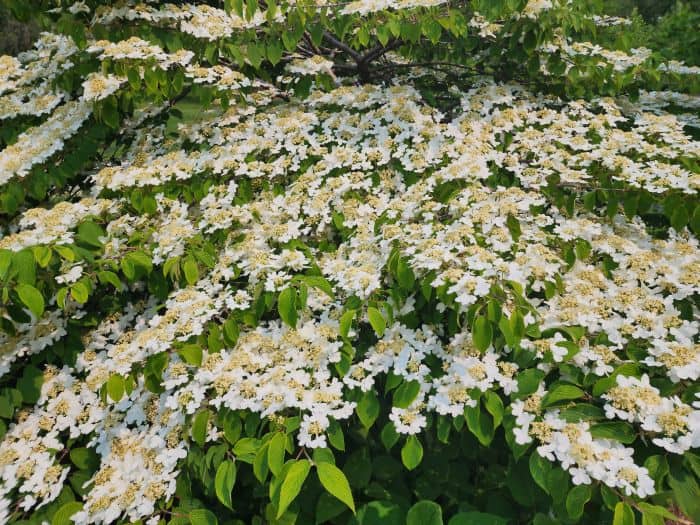
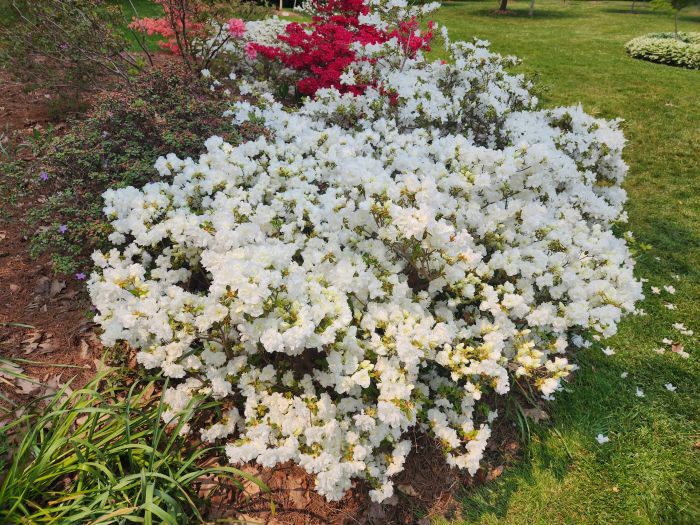
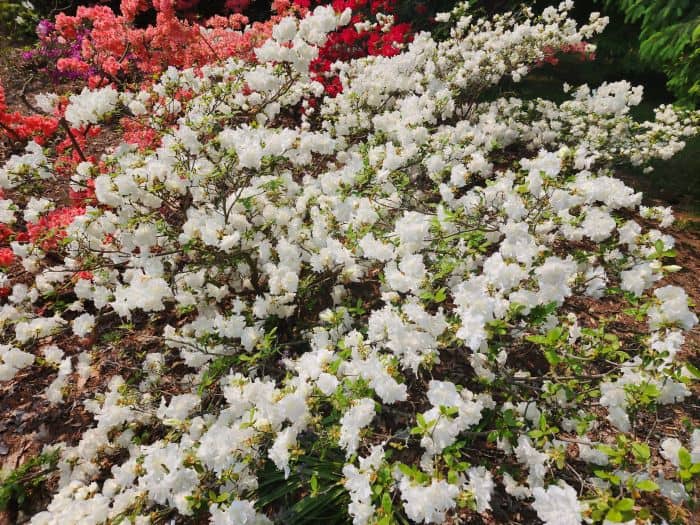
Azaleas, a captivating and vibrant species of flowering shrubs, have a rich history that dates back centuries. Originating mostly from Asia and North America, these flowering plants have stunning blooms and lush foliage. The name “Azalea” is derived from the Greek word “azaleos“, which means “dry“.
Azaleas hold an important place in the realm of gardening. Their striking colors and the ability to bloom generously make them a favorite among garden enthusiasts and landscape artists. They are often used as standalone specimens, in group plantings, or stunning borders and hedges. In addition, azaleas symbolize homecoming and passion, making them a popular choice in cultural festivals and events.
In the gardening world, gardeners celebrate azaleas for their adaptability and resilience. They can thrive in all climates, from the cool Himalayas regions to Australia’s subtropical zones.
Types of Azaleas
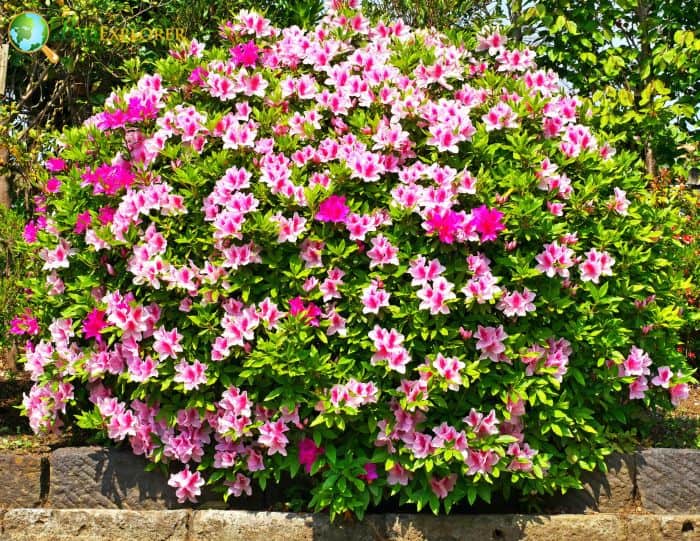

Azaleas are a fascinating subset of the Rhododendron genus, represented by over 800 species. Among these, approximately 75 species are classified as azaleas. These beautiful flowering shrubs are generally grouped into three main categories: Evergreen Azaleas, Deciduous Azaleas, and Exotic Azaleas.
- Evergreen Azaleas are celebrated for their perpetual foliage, maintaining their greenery throughout the year. They are primarily native to Japan and are popular for their dense flowering and diverse color range. These azaleas bloom in various colors, including white, pink, red, and purple.
- Deciduous Azaleas, conversely, are native to North America, Europe, and Asia. These fragrant flowers wither their leaves in the fall to reveal a beautiful range of autumn colors before they go dormant for the winter.
- Lastly, Exotic Azaleas refer to the unique and rare varieties of azaleas not commonly found in traditional gardens. These exotic flowers include the Rhododendron oldhamii (Fourth of July Azalea) and the Rhododendron occidentale (Western Azalea).
Evergreen Azaleas
Evergreen Azaleas are admired for their year-round foliage and dense flowering[1]. Here are ten notable species:

- Rhododendron simsii: Known as the Sims’s azalea, it produces vibrant red flowers and is often used as an indoor plant due to its compact size and striking blooms.

- Rhododendron indicum: This species is admired for its large, showy flowers that come in a variety of colors, including pink, red, and white. The flowers often have a slight fragrance, adding to their appeal.

- Rhododendron obtusum: Also known as the Hiryu azalea, it is renowned for its striking crimson flowers. The blooms are typically single and appear in clusters, creating a vibrant display.

- Rhododendron kiusianum: This species, native to Japan, is a dwarf azalea with pink to purple flowers. Despite its small size, it produces abundant blooms covering the entire plant.
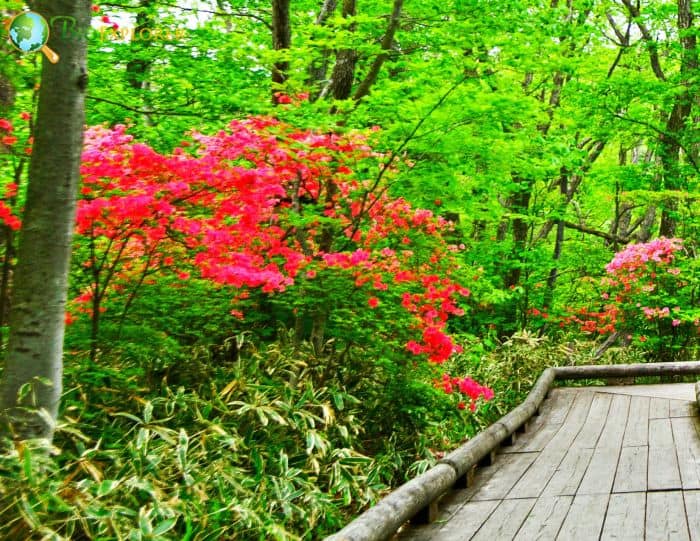

- Rhododendron kaempferi: The Torch azalea is known for its bright orange-red flowers. The blooms are bell-shaped and appear in clusters, creating a fiery display.
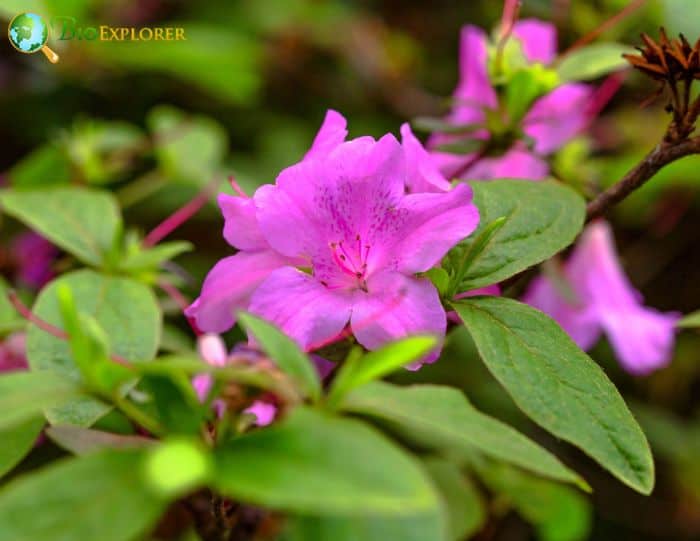

- Rhododendron yedoense: This species, also known as the Yodogawa azalea, has vibrant purple flowers. The blooms are typically single and have a slight fragrance.
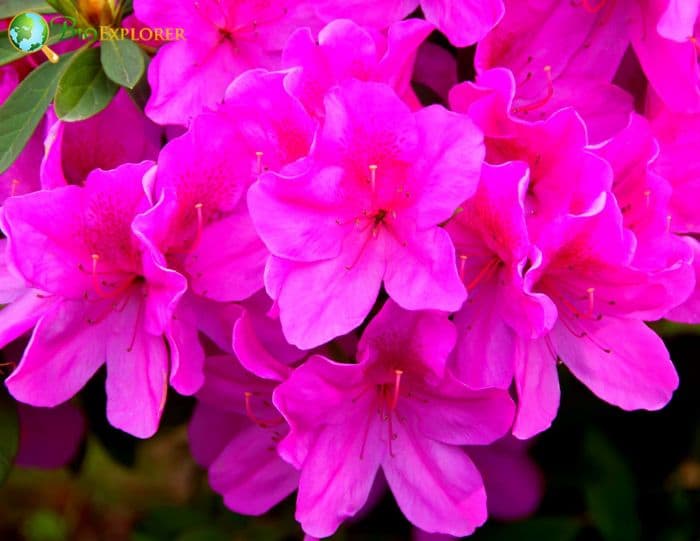

- Rhododendron ‘Amoena’: This hybrid azalea is popular for its small, dark pink flowers. The blooms are double, giving them a fuller appearance.
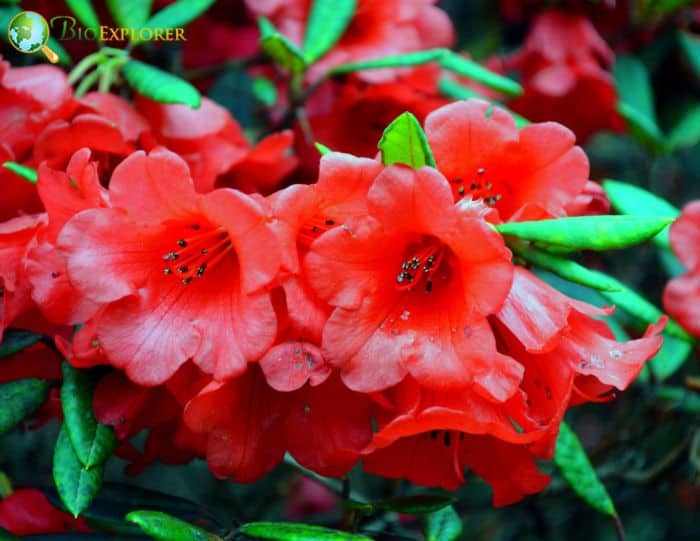

- Rhododendron ‘Hino-crimson’: This compact azalea is known for its single, vibrant red flowers. Despite its small size, it produces a profusion of blooms that create a stunning display.
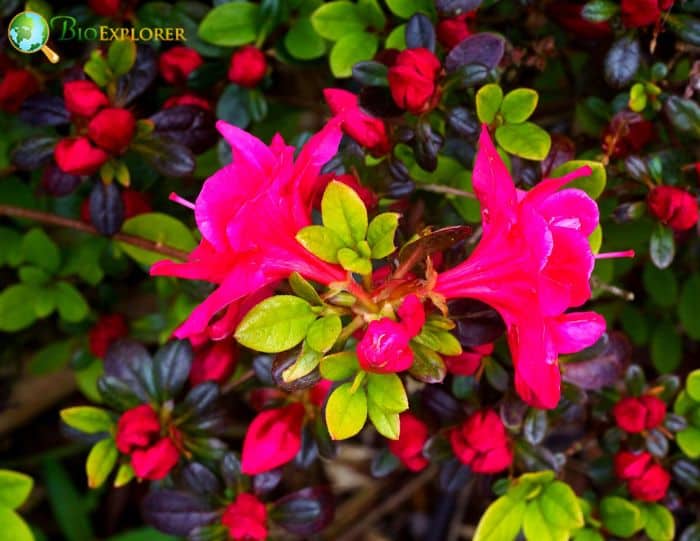

- Rhododendron ‘Hershey’s Red’: This species is admired for its deep red flowers and dark green foliage. The contrast between the blooms and the foliage creates a striking display.
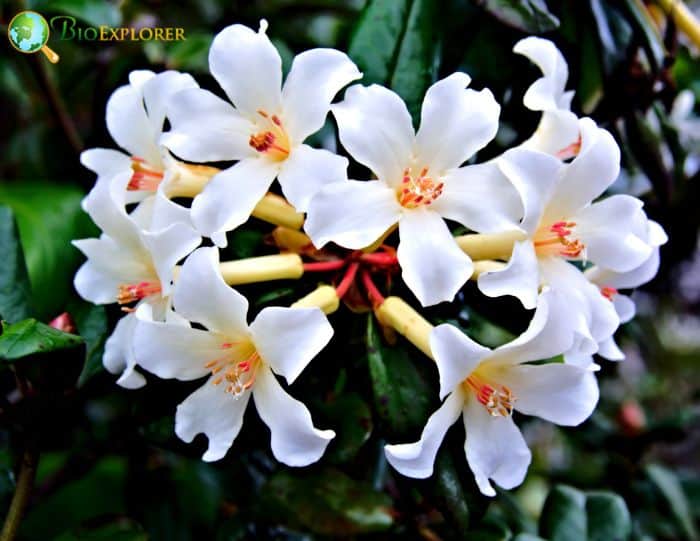

- Rhododendron ‘Gumpo White’: This low-growing azalea produces large, white flowers. The blooms appear in clusters and contrast beautifully with the dark green foliage.
Deciduous Azaleas
Deciduous Azaleas are known for their vibrant[2] and often fragrant flowers. Here are ten notable species:
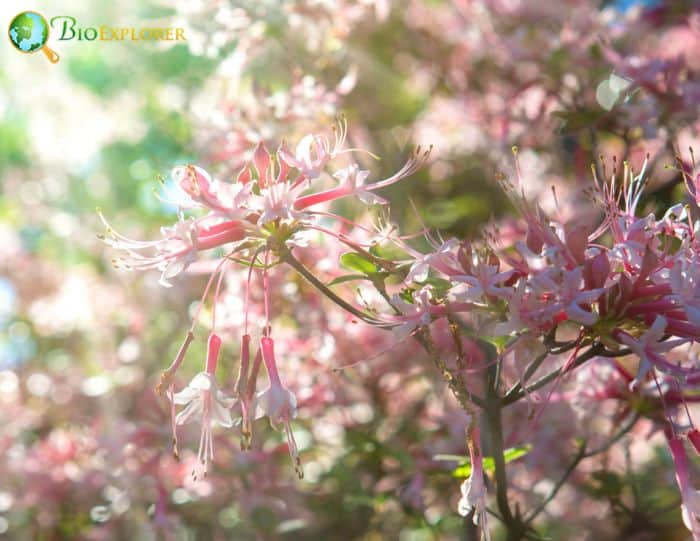

- Rhododendron canescens: Known as the Piedmont azalea, it produces fragrant pink flowers. The blooms are typically tubular and appear in clusters, creating a stunning display in the Spring.
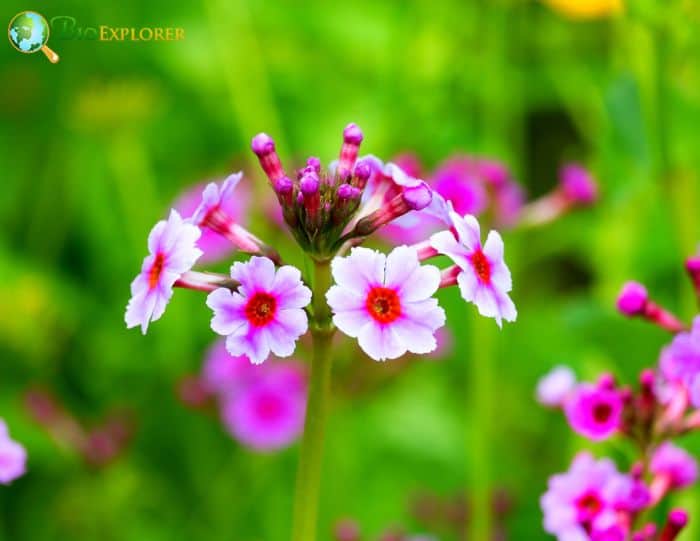

- Rhododendron atlanticum: The Coastal azalea is known for its spicy-scented white or pink flowers. The blooms are typically smaller and more delicate than other azaleas, adding a subtle charm to any garden.
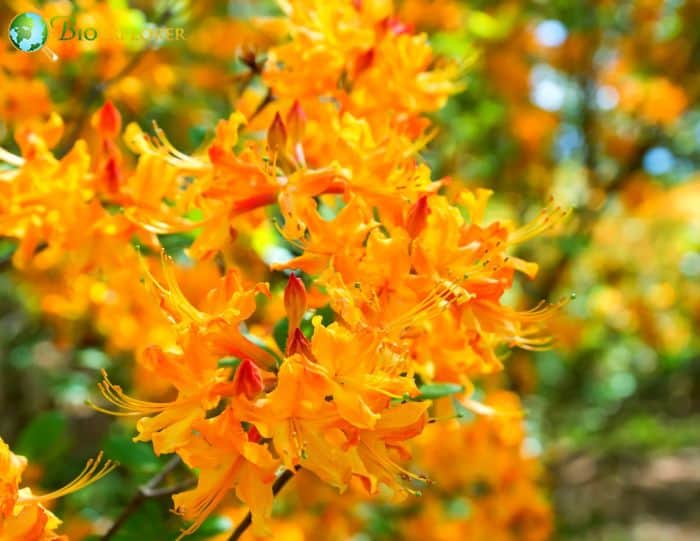

- Rhododendron austrinum: Also known as the Florida azalea, it is admired for its bright orange-yellow flowers. The blooms are typically larger and have a strong, pleasant fragrance.
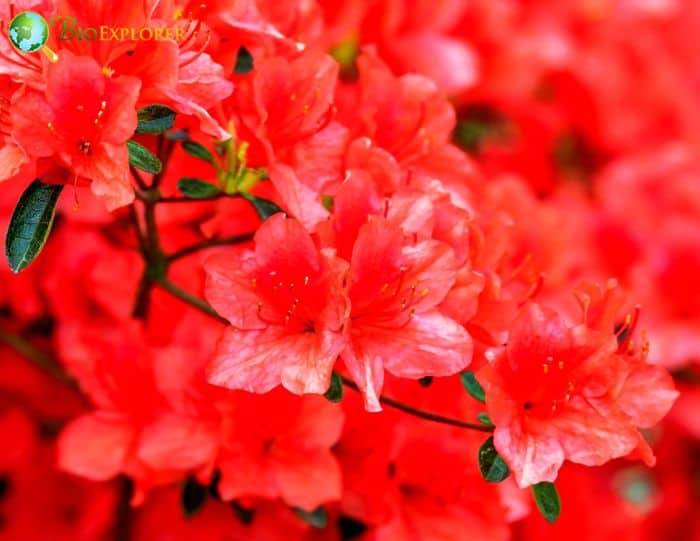

- Rhododendron calendulaceum: The Flame azalea is known for its large, bright orange and red flowers. The blooms are typically tubular and appear in clusters, creating a fiery display in the Spring.
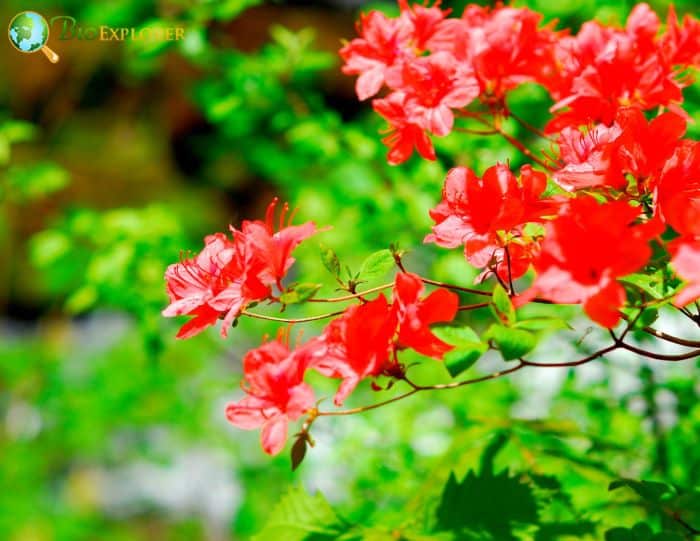

- Rhododendron cumberlandense: Also known as the Cumberland azalea, it produces orange to red flowers. The blooms are typically smaller and appear in clusters, creating a vibrant display.
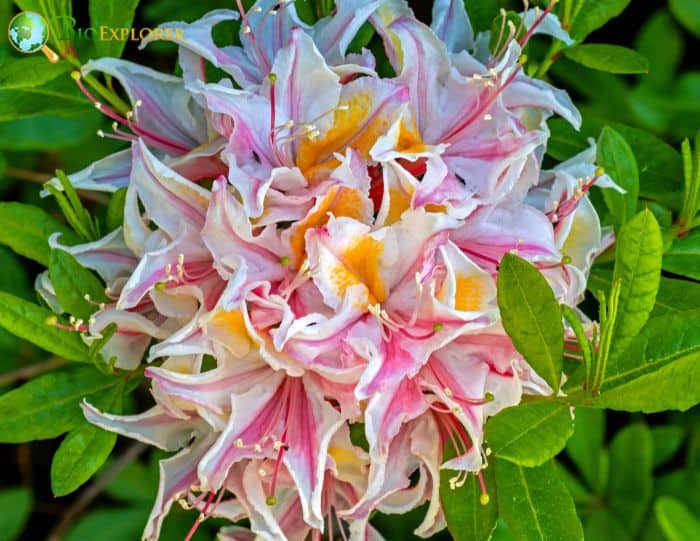

- Rhododendron occidentale: The Western azalea is known for its large, fragrant, pink-to-white flowers. The blooms are typically larger and have a strong, pleasant fragrance.
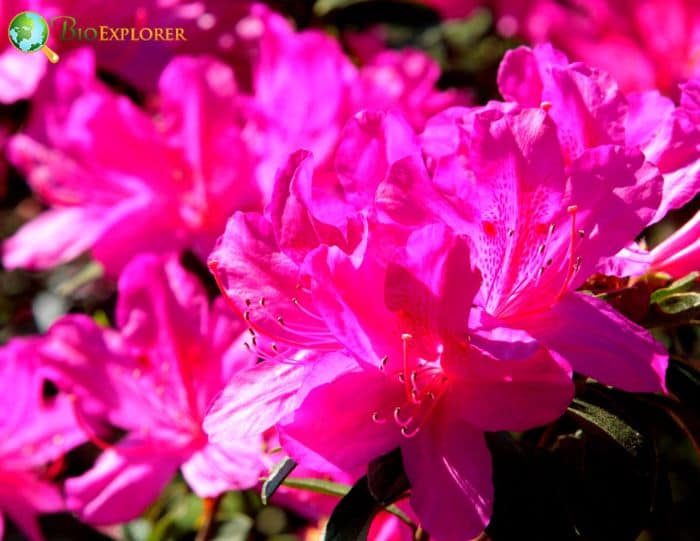

- Rhododendron periclymenoides: Also known as the Pink azalea, it produces pink to white flowers. The blooms are typically tubular and appear in clusters, creating a stunning display in the Spring.
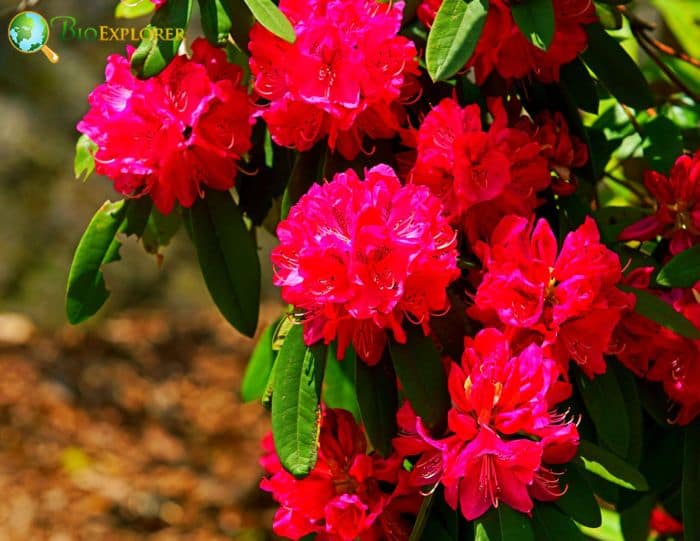

- Rhododendron prinophyllum: The Roseshell azalea is known for its Rose-purple flowers with a spicy scent. The blooms are typically larger and appear in clusters, creating a vibrant display.
- Rhododendron viscosum: The Swamp azalea is known for its fragrant white flowers. The blooms are typically smaller and more delicate, adding a subtle charm to any garden.
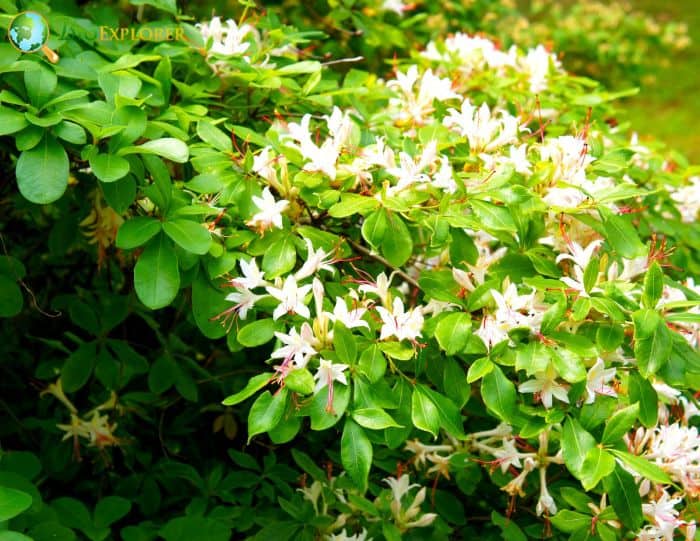

- Rhododendron arborescens: The Sweet azalea is admired for its white, fragrant flowers and prominent red stamen. The blooms are typically larger and have a strong, pleasant fragrance.
Exotic Azaleas
Exotic Azaleas refer to the unique and rare varieties[3] of azaleas not commonly found in traditional gardens. Here are 10 notable species:
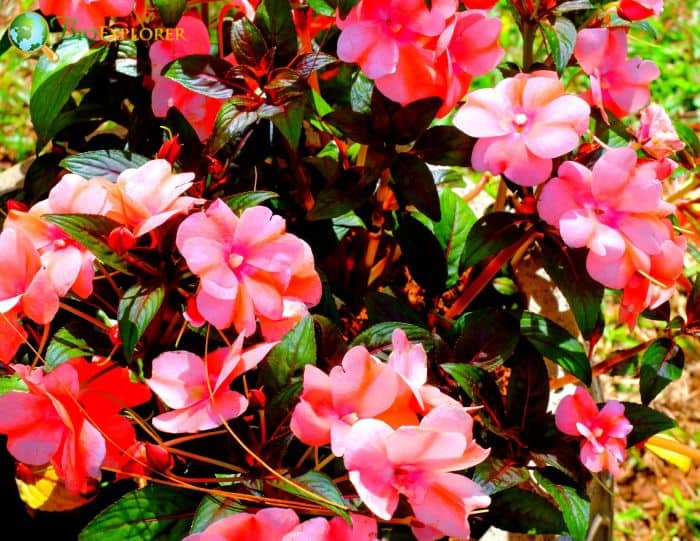

- Rhododendron oldhamii: The Fourth of July Azalea is known for its early summer blooms. The flowers are typically orange-red and have a pleasant fragrance.
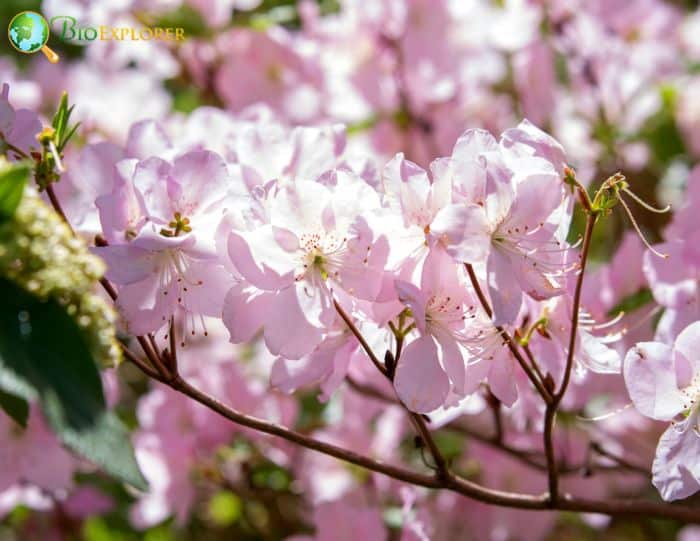

- Rhododendron schlippenbachii: The Royal Azalea is known for its large, pink flowers. The blooms are typically larger and have a strong, pleasant fragrance.
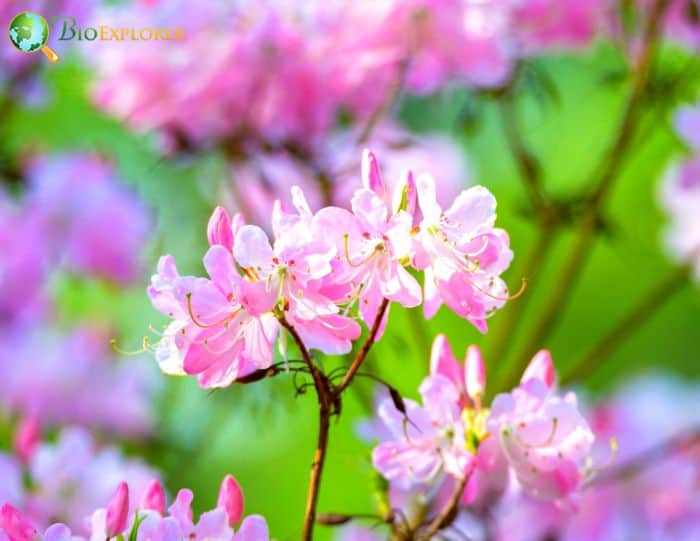

- Rhododendron vaseyi: The Pinkshell Azalea is known for its delicate pink flowers. The blooms are typically smaller and appear in clusters, creating a stunning display in the Spring.
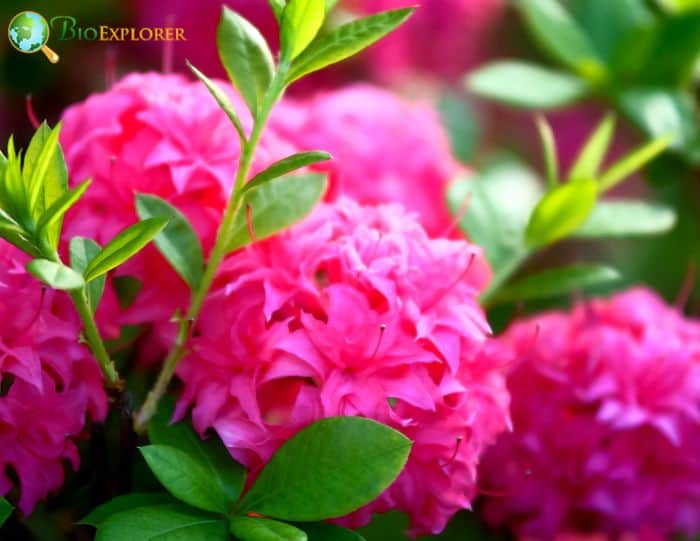

- Rhododendron ‘Homebush’: This hybrid azalea is known for its double pink flowers. The blooms are typically larger and appear in clusters, creating a stunning display.
- Rhododendron ‘Koromo Shikibu’: This hybrid azalea is known for its unique, spider-like lavender flowers. The blooms are typically smaller and appear in clusters, creating a unique display.
- Rhododendron ‘Ben Morrison’: This hybrid azalea is known for its large, fragrant, pink flowers. The blooms are typically larger and have a strong, pleasant fragrance.
- Rhododendron ‘Golden Oriole’: This hybrid azalea is known for its vibrant orange flowers. The blooms are typically larger and appear in clusters, creating a vibrant display.
- Rhododendron ‘Irohayama’: This hybrid azalea is known for its vibrant red flowers. The blooms are typically larger and appear in clusters, creating a vibrant display.
- Rhododendron ‘Shinnyo no Tsuki’: This hybrid azalea is known for its large, white flowers with a pink edge. The blooms are typically larger and appear in clusters, creating a stunning display.
Understanding Azalea Plant Features
Azaleas are renowned for their captivating beauty and diverse features. Understanding these characteristics[4] can help you appreciate these plants even more and provide them with the best care.
| Size | Azaleas are generally small to medium-sized shrubs, typically growing between 1 to 8 feet tall, depending on the species and variety. |
| Leaves | Azaleas have small, oval-shaped leaves that are often glossy green. The leaves of evergreen azaleas stay green throughout the year. In contrast, those deciduous azaleas change color in the fall before dropping. |
| Flowers | The flowers of azaleas are their most striking feature. With five petal-like lobes, these flowers can range from 1 to 2 inches in diameter. |
| Colors | The flowers can be white, pink, red, purple, orange, or a combination of these colors. Some hybrids have single-color while others have bi-color or multi-color in some crossbreeds. |
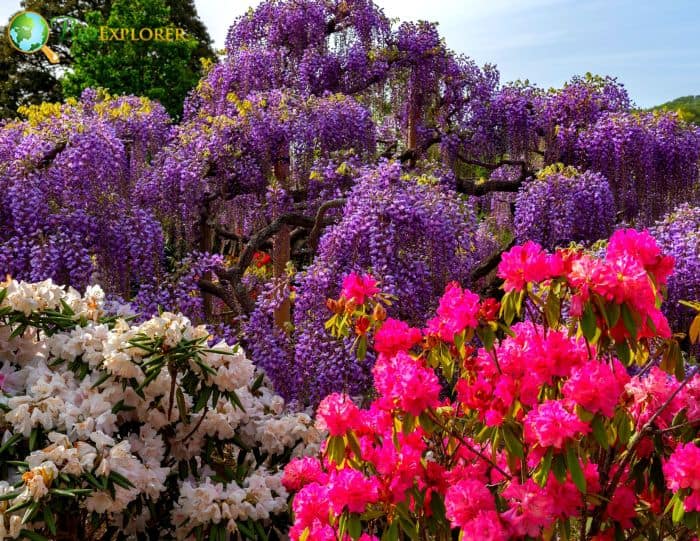
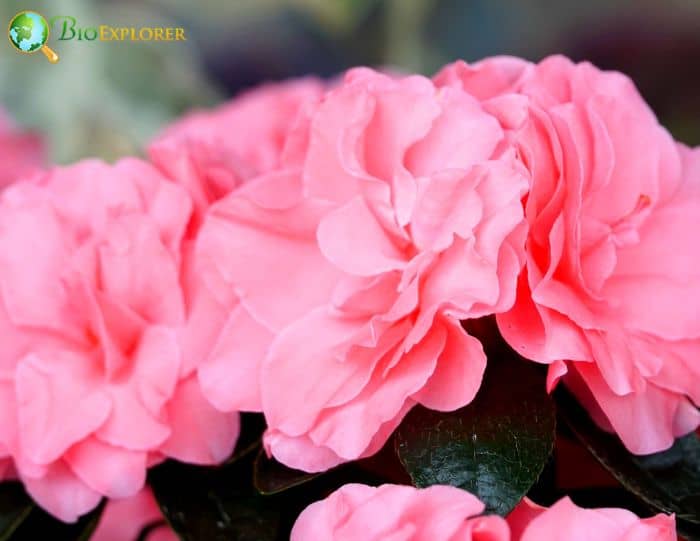
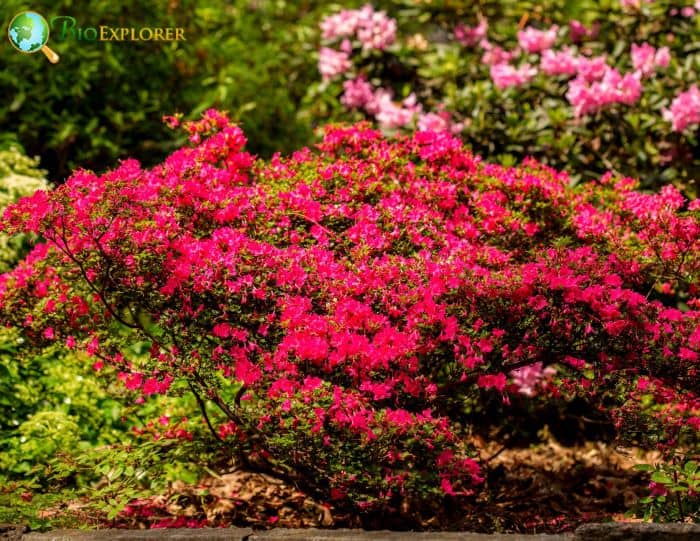
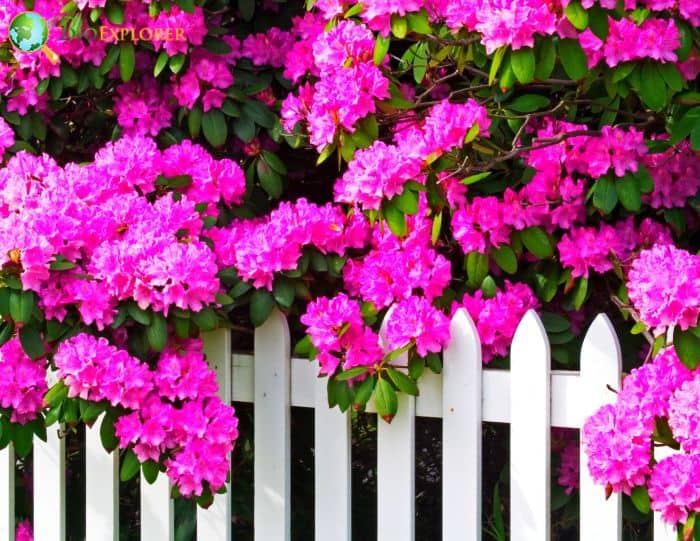
Azalea Pictures
How to Plant Azaleas?
Planting azaleas involves several steps, from choosing the correct location to preparing the soil and the actual planting process. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to plant azaleas:
- Choose the right location: Azaleas prefer a spot that receives partial shade to full sun, with at least 4 to 6 hours of direct sunlight daily. However, in hotter climates, consider putting them in the shade during the hottest part of the day. The location should also have good drainage to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot.
- Prepare the soil: Azaleas prefer slightly acidic soil rich in organic matter. If your garden soil is either sandy or heavy clay, its fertility, and texture can be enhanced by incorporating organic materials like compost or thoroughly decomposed manure. If your soil isn’t acidic enough, consider using a soil acidifier.
- Dig a hole: When preparing to plant an azalea, it is recommended to dig a hole that is double the width and equal in depth to the plant’s root ball.
- Plant the azalea: Place the azalea in the hole, ensuring the top of the root ball is level with the soil surface. Fill the hole with soil and gently tamp it down.
- Water the azalea: Water the plant thoroughly after planting and keep the soil moist but not waterlogged.
- Mulch the azalea: By adding a 3-inch layer of organic mulch, it retains soil moisture and keep soil temperatures from fluctuating.
- Care for the azalea: Azaleas must be watered regularly, especially during dry spells. They also benefit from occasional fertilization and pruning.
Azalea Care Guide
Azaleas are relatively easy to care for once established. However, they require attention to remain healthy and produce abundant blooms. Here’s a guide on how to care[5] for azaleas:
Watering Requirements and Schedule
- Azaleas prefer consistently moist soil, but avoiding overwatering is important as this can lead to root rot. Water your azaleas regularly During the growing season, especially during dry spells.
- To maintain optimal moisture levels for your azalea, a useful guideline is to provide deep watering at least once a week or increase the frequency during intense heat and dry conditions.
- However, always check the soil moisture levels before watering. Ensure the soil remains moist for optimal plant growth and is not excessively saturated or soggy.
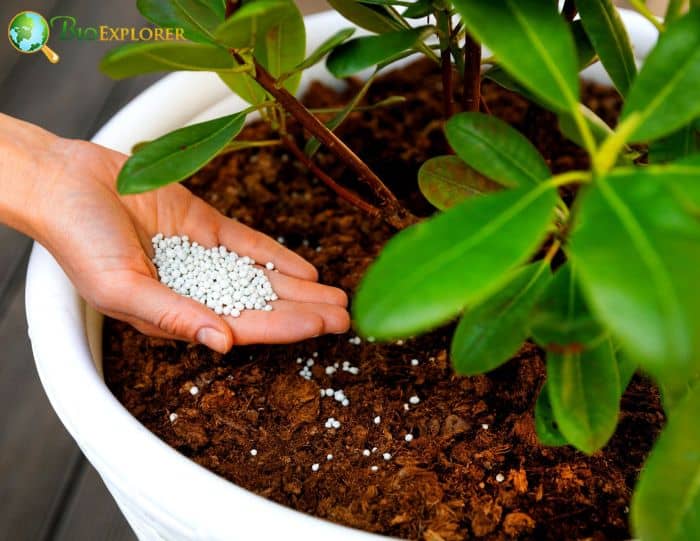
Fertilizer Needs and Application
- Azaleas benefit from regular feeding. Use a slow-release, granular fertilizer specially formulated for acid-loving plants, such as azaleas and rhododendrons.
- As the plant emerges from hibernation in Spring, apply the fertilizer just before the new growth begins. Avoid applying fertilizer after mid-summer, as this can stimulate new growth that may not harden off before winter.
Pruning and Maintenance Tips
Pruning[6] is not usually necessary for azaleas, as they naturally grow into a pleasing shape. However, you can prune them to maintain their size or to remove dead or diseased stem/wood.
- The best time to prune azaleas is in late Spring, just after they finish blooming. This is because azaleas set their flower buds for the next year in the summer, so late pruning can remove these buds and reduce the next year’s blooms.
- In terms of maintenance, applying a layer of organic mulch around your azaleas every Spring is a good idea. This helps conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and add nutrients to the soil. Keep the mulch a few inches from the plant’s trunk to prevent rot.
- Finally, keep an eye out for pests and diseases. Azaleas can be affected by several pests, such as lace bugs and azalea borers, and diseases, such as leaf gall and petal blight. If you notice any signs of pests or diseases, take action promptly to prevent them from spreading.
Azalea Common Pests and Diseases
Like all plants, Azaleas can be susceptible to certain pests and diseases. Here’s a brief overview of the most common issues and how to deal with them:
Common Pests
- Azalea Lace Bugs: Lace bugs, pesky insects known for their tendency to feed on the undersides of leaves, can cause unsightly yellowing and speckling. To effectively manage lace bug infestations, options include insecticidal soap or systemic insecticides.
- Azalea Borers: These pests bore into the stems, causing wilting and death of branches. Prune and destroy infested branches and consider using a suitable insecticide.
Common Diseases
- Leaf Gall: A fungal disease that can result in distorted and swollen leaves. To prevent the spread of the disease, it is advisable to promptly remove and dispose of the infected leaves.
- Petal Blight: This disease causes flowers to become spotted and mushy. To control petal blight, remove and destroy affected flowers and apply a fungicide.
Prevention and Treatment
- Regular monitoring prevents and treats pests and diseases. Inspect your azaleas regularly for signs of trouble, and take action promptly if you notice anything unusual.
- Maintaining good cultural practices can also help prevent problems. This includes watering properly, avoiding overhead watering, maintaining good air circulation around plants, and cleaning up plant debris.
- If pests or diseases become a serious problem, consider seeking advice from a local extension service or a professional horticulturist. They can provide specific recommendations based on your local conditions and the specific problems your azaleas are facing.
Propagation of Azaleas
Azaleas can be propagated through several methods:
- Cuttings: This is the most common method of propagating azaleas. Semi-hardwood cuttings are taken in late summer or early fall, treated with rooting hormone, and planted in a well-draining medium.
- Layering: This involves bending a low-growing branch to the ground, covering part of it with soil, and then severing the rooted part from the parent plant after roots have formed.
- Seeds: Azaleas can also be grown from seeds, but this method is less common as it requires more time, and the resulting plants may not be identical to the parent plant.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where is the best place to plant an azalea?
Do azaleas come back every year?
Where should you not plant azaleas?
Are azaleas hard to take care of?
Cite This Page
Viewed using Just Read